Introduction to SQL Server DENSE_RANK() function
The DENSE_RANK() is a window function that assigns a rank to each row within a partition of a result set. Unlike the RANK() function, the DENSE_RANK() function returns consecutive rank values. Rows in each partition receive the same ranks if they have the same values.
The syntax of the DENSE_RANK() function is as follows:
DENSE_RANK() OVER (
[PARTITION BY partition_expression, ... ]
ORDER BY sort_expression [ASC | DESC], ...
)
The DENSE_RANK() function is applied to the rows of each partition defined by the PARTITION BY clause, in a specified order, defined by ORDER BY clause. It resets the rank when the partition boundary is crossed.
The PARITION BY clause is optional. If you omit it, the function will treat the whole result set as a single partition.
SQL Server DENSE_RANK() function illustration
The following statements create a new table named dense_rank_demo and insert some rows into that table:
CREATE TABLE sales.dense_rank_demo (
v VARCHAR(10)
);
INSERT INTO sales.dense_rank_demo(v)
VALUES('A'),('B'),('B'),('C'),('C'),('D'),('E');
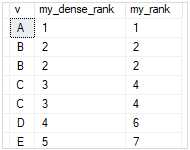
SELECT * FROM sales.dense_rank_demo;
The following statement uses both DENSE_RANK() and RANK() functions to assign a rank to each row of the result set:
SELECT
v,
DENSE_RANK() OVER (
ORDER BY v
) my_dense_rank,
RANK() OVER (
ORDER BY v
) my_rank
FROM
sales.dense_rank_demo;
SQL Server DENSE_RANK() function examples
We will use the production.products table to demonstrate the DENSE_RANK() function:

Using SQL Server DENSE_RANK() over a result set example
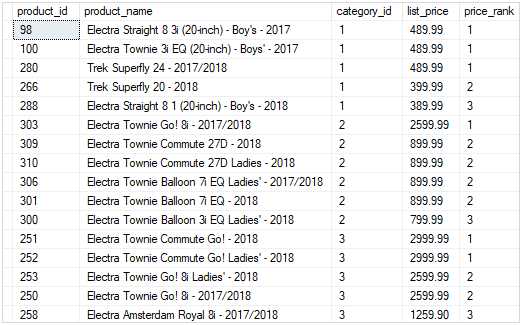
The following example uses the DENSE_RANK() function to rank products by list prices:
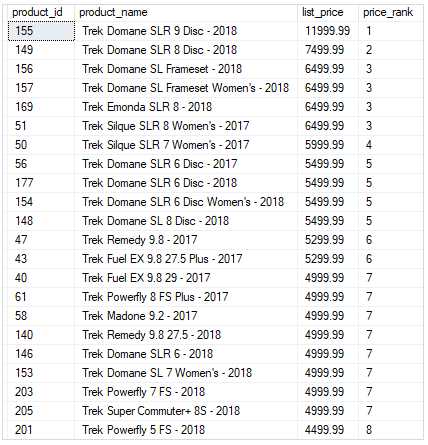
Using SQL Server DENSE_RANK() over partitions example
The following statement ranks products in each category by list prices. It returns only the top 3 products per category by list prices.
SELECT * FROM (
SELECT
product_id,
product_name,
category_id,
list_price,
DENSE_RANK () OVER (
PARTITION BY category_id
ORDER BY list_price DESC
) price_rank
FROM
production.products
) t
WHERE price_rank < 3;
DENSE_RANK() function to assign a rank to each row within a partition of a result set, with no gaps in rank values.